Preventive Maintenance for manufacturing explained
Learn about preventive maintenance in manufacturing, its benefits, drawbacks, and how it differs from predictive maintenance in this in-depth article.

In the dynamic world of manufacturing, where every moment counts, efficiency and productivity are paramount. One of the most effective strategies to ensure smooth operations and prevent unexpected downtimes is preventive maintenance.
This approach focuses on proactive measures to maintain equipment and prevent premature failures.
In this article, we will answer the question: what is preventive maintenance? Read on to delve into common types of maintenance, how preventive maintenance benefits manufacturing, and future trends in preventive maintenance.
Types of maintenance in manufacturing
Manufacturing processes heavily rely on machinery and equipment, and the way these assets are maintained greatly influences overall efficiency. There are three main types of maintenance practices in manufacturing:
- Reactive Maintenance: This approach involves addressing issues only after equipment failures occur, leading to unplanned downtimes and productivity setbacks.
- Preventive Maintenance: With preventive maintenance, equipment is regularly maintained on a schedule based on time, usage, or other relevant factors, reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns.
- Predictive Maintenance: This data-driven approach uses real-time information and preset parameters to predict when maintenance is required, allowing for precise scheduling and reduced downtime.
What is preventive maintenance?
Preventive maintenance (sometimes written as preventative maintenance) is a proactive approach to maintenance that involves maintaining equipment while it's still operational and functioning smoothly, thereby preventing critical failures.
Instead of waiting for machines to break down, preventive maintenance involves timely inspections, adjustments, and repairs to ensure that everything operates optimally.
Two common ways to plan preventive maintenance are:
- Calendar Time: Maintenance tasks are scheduled based on a fixed calendar timeline (days, weeks, months). While this is better than reactive maintenance, it might not always be the most efficient approach.
- Runtime or Cycles: Maintenance tasks are scheduled based on equipment usage (hours in use) or counted cycles (units produced, batches made). This approach ensures that maintenance occurs when it's actually needed, rather than relying on a predefined calendar. This approach works best when you use a solution that gives you live and accurate production data.
Predictive maintenance vs preventive maintenance
Predictive maintenance and preventive maintenance are two distinct maintenance strategies that people often find confusing.
As described above, preventive maintenance involves scheduled routine checks and servicing of equipment based on predetermined time intervals or usage counts.
On the other hand, predictive maintenance detects subtle changes and anomalies, anticipating failures and recommending maintenance actions just in time, further optimizing resource allocation and minimizing disruption.
In essence, preventive maintenance is a proactive, time-based strategy, whereas predictive maintenance is more data-driven.
Benefits and drawbacks of preventive maintenance
Preventive maintenance is an effective, low-cost, and easy-to-implement process that reduces the chances of premature equipment failure in manufacturing.
Benefits:
- Less unplanned downtime: By addressing potential issues before they lead to failures, preventive maintenance significantly reduces unplanned downtime for more continuous production.
- Extended equipment life: Regular maintenance helps extend the useful lifespan of equipment, delaying the need for costly replacements and increasing ROI.
- Relatively easy implementation: Preventive maintenance can be implemented without complex data analysis and expensive equipment, making it accessible to a wide range of manufacturing setups.
- Increased profits: Improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and longer equipment lifespans should contribute to higher profits for manufacturers.
Learn how Royal Unibrew improved maintenance processes and increased line output by 14%: Read the case story.
Drawbacks:
- Failures can still occur: Despite preventive measures, equipment failures can still happen due to unforeseen circumstances, human error, and hidden issues.
- Unnecessary maintenance: Maintenance might occur too frequently, leading to the wastage of resources.
- Incidental damage: During maintenance, there's a possibility of incidental damage to other components, which is especially costly if maintenance is too frequent.
Preventive maintenance trends
As the manufacturing landscape evolves, so do maintenance practices. One notable trend is the shift towards operator-driven maintenance. Manufacturers are empowering their operators with proper training and tools to handle simple maintenance tasks, such as cleaning, that can be performed based on equipment usage counts. This not only frees up the maintenance team's capacity but also ensures that routine tasks are handled efficiently.
Operator-driven maintenance involves operators taking on tasks triggered by factors like product counts passing through a machine. For instance, an operator might clean a gluing station after a specific duration of operation or lubricate a filling machine after a certain number of products have been produced. This trend enables engineers and technicians to focus on more complex issues that require their specialized skills.
Moreover, there’s a broader trend towards upskilling operators for preventive maintenance tasks. This trend aligns with the concept of "lights-out" manufacturing, where automation and advanced technology allow production to continue with minimal human intervention.
As preventive maintenance becomes operator-driven, predictive maintenance becomes the domain of engineers and technicians, who analyze data and set parameters for optimal performance.
How to get started with preventive maintenance
In the competitive realm of manufacturing, every minute counts, and downtime can have a significant impact on productivity and profitability.
Fortunately, implementing preventive maintenance doesn't have to be complicated. Plug-and-play solutions like Factbird's Preventive Maintenance Module offer a seamless way to integrate this strategy into your manufacturing process.
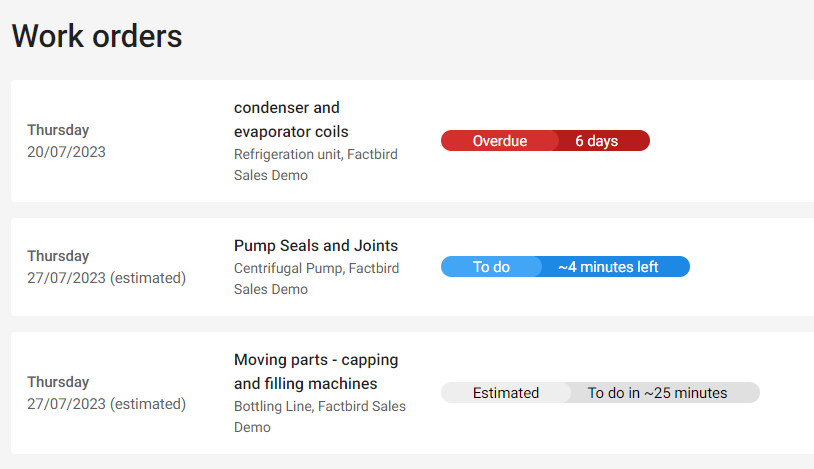
The Preventive Maintenance Module lets you focus on counts as well as calendar time, making it versatile and powerful plug-and-play solution that harnesses live production data. Unlike traditional CMMS systems that require manual data entry or complex integrations, this approach streamlines the preventive maintenance process.

